Ο coronavirus is a big puzzle for the global medical community, but it can also prove to be another important working hypothesis about how the world economy works at a time when everything is interconnected.
In fact, a fitting journalistic headline would be "How a wild animal in a Chinese market can shake the foundations of the global economic system."
New Year for the Chinese was not very lucky this year, as the appearance and spread of the coronavirus spread a "dark veil" over the country with 1.386 billion inhabitants, which is the second strongest economy on the planet.
It remains to be seen whether the Chinese dragon will be the only one affected by the virus or whether we should all worry about our pockets, except our health.
Human psychology and in particular fear is a central factor in shaping financial figures, no matter how out of place it sounds to some. Accordingly, the transparency with which the authorities will deal with the spread of the coronavirus (Covid-19) will play an important role in the long-term "recovery" of economies.
Η Uhan of Hubei Province has emerged as the Ground Zero of the virus, in Chernobyl, China, to cover both sides of the once Cold War Curtain. The city has been stained and turned into a deserted battlefield, where the coronavirus has hit hard. But its importance to the Chinese economy is inversely proportional to its current image.

Wuhan, with a population of about 11 million people, is a magnet for foreign investment with developed trade, industry and exports, making it a hub for the country's economy. It was also acknowledged by President Xi Jinping.
Overall, China has seen unprecedented growth over the past 40 years, bringing it just behind the US in the world's strongest economies with annual growth of more than 7%. This happened because it surpassed the "American eagle" in world trade and with a huge domestic market, became the Promised Land for international capital. It is also the hub of a global supply chain, with many raw materials traveling to China before being turned into a product.
Competition with the US peaked when Donald Trump became a resident of the White House, and was transformed into a trade war with the threat of tariffs on both sides in the movement of goods.

Economists cannot predict the exact consequences of an epidemic. However, epidemics can be more damaging than a natural disaster, such as a tsunami or a hurricane. According to a study by the World Bank, a serious pandemic could cause economic losses of 5% of world GDP, which translates to more than $ 3 trillion.
Coronavirus could affect China's Gross Domestic Product by up to 4% in the first quarter of 2020, and before the outbreak, the Chinese government estimated growth of 6% year-on-year. International analysts are revising the figure to 5%, predicting that the economy will recover from next fall. But these are just assumptions.
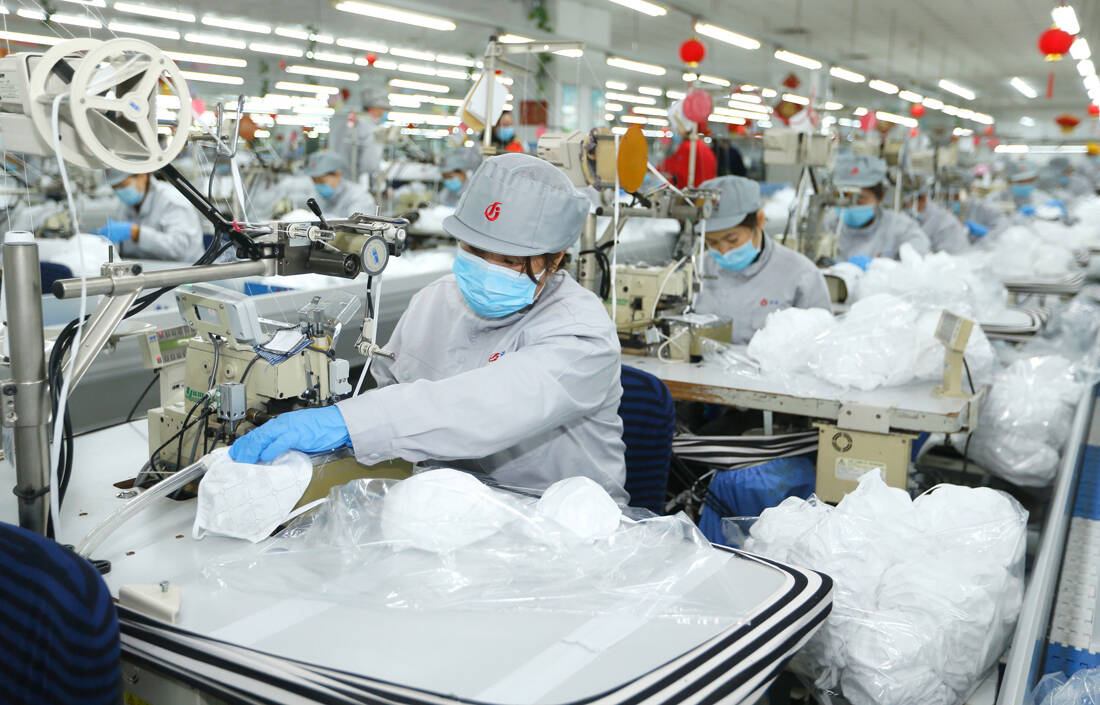
Many businesses in China remain closed for fear of proliferation, automakers are closing factories and ports are much quieter than ever. Of course the impact that the alarm situation has on consumers is huge, creating a market stoppage with unpredictable dimensions and duration.
China has become an integral part of the global economy since the SARS outbreak in 2003, when its impact was 4% of total GDP, while in 2017 it reached 15%. Globalization has encouraged companies to build cross-border supply chains that increasingly entangle national economies.
The coronavirus spreads 6 times faster than SARS, mainly through human contact. The numbers look alarming. The areas that have been primarily affected by the disease are travel and the tourism industry in China, Asia and around the world, as the Chinese have for years accounted for a large part of the tourist "pie".
Neil Shearing, chief analyst at Capital Economics, said: "Traveler numbers have fallen by 55% this season. "And since the Chinese are spending a lot of money, the cost of the travel ban will be felt."

But tourism is just the beginning. The automotive, electronics and shipping industries are falling sharply. The same goes for the food and beverage retail trade. Even the price of coffee in the country was affected, with half of the approximately 4.000 Starbucks stores remaining closed.
At the same time multinational companies rely on supplies from China. For example, 290 of Apple's 800 suppliers are based in the country. Automotive executives in Europe and the US warn of shortages in the coming weeks. Hyundai has already stopped operating in South Korea due to shortages of various parts of cars coming from China.
After Chinese New Year, car factories were closed with companies such as Volkswagen, Toyota, Renault, General Motors, Honda and Hyundai unable to continue their operations in the world's largest car market. The spread of the virus will force the car industry to reduce its production by 15% in the first quarter of 2020. In fact, Toyota announced that it will keep factories closed until February 17.
Chinese consumer-based luxury goods companies staying at home instead of shopping have also been hit. Britain's Burberry has closed 24 of its 64 stores in China while international airlines are canceling flights to and from China.
The problem is even bigger for international supply chains. Qualcomm, the largest maker of smartphone chips, has warned that the outbreak of the virus is causing uncertainty in the mobile phone market.
Stock markets in Asia have fallen sharply in recent days and oil prices have also come under pressure, due to an expected drop in demand.

"The new coronavirus will have a significant impact on oil demand, the forecast for which has been sharply revised downwards this year," the International Energy Agency (IEA) has warned.
In this context, the IEA revised down by 365.000 barrels per day its expectations for an increase in demand for crude oil in 2020, which is now expected to be 825.000 barrels per day, at the lowest point since 2011, and predicts a decline in demand in the first quarter, for the first time in over a decade.
Demand is expected to fall by 435.000 barrels a day in the first quarter.
"It simply came to our notice then Covid-19 in global oil demand will be significant ", the IEA estimates in its monthly report on oil.
The strong economies of the world are also experiencing those shocks from the spread of the virus. Neighboring Japan is exposed, as China is the largest buyer of industrial machinery, cars and high-tech products. Not to mention the fact that there have already been 400.000 cancellations for the first quarter of 2020 by Chinese travelers.
Η Australia It is also closely linked to China, with Prime Minister Scott Morrison warning of a "real burden on the economy". Even the country's universities are suffering, as many fewer Chinese students have returned and paid tuition for the new academic year.
As for Great Britain, the big malls seem to be affected by the fact that they will not have the usual Chinese customers. However, the real threat to Britain, Europe and the US is the possibility of a slowdown in world trade. The interdependence of the economies is so great that if "China sneezes, the world economy will cool down," writes CNN.
Accordingly, US companies will find it difficult to access components for manufacturing products, with the risk that the sector will enter the state of recession in which it had fallen last year. Which may have a political imprint on Trump's bid for re-election, as he has a central campaign slogan of creating jobs in industries in states hit by the recession.
The coronavirus is a threat to the Greek economy, even if it seems to be on the rise. The global crisis is expected to cost $ 300 billion to $ 450 billion, based on mild scenarios, or 0,3% to 0,4% of world GDP.
The sectors that can be affected - and are already affected - in Greece are mainly tourism and the real estate market. The overall impact will, however, depend on how long the virus has been spreading and how governments are handling the issue. However, in a country that relies heavily on the benefits of tourism and where the real estate industry is on the rise, China's momentum is likely to affect the economy as a whole.

At the same time, the European Commission maintains the forecast for economic growth in 1,2 and 2020 in the eurozone at 2021%, but warns of the uncertainty associated with the epidemic. Covid-19.
"Its appearance and dispersion Covid-19 "and its effects on public health, human lives and economic activity are a source of growing concern," the European Commission said in a statement.
"Right now, we assume that China's GDP will be the hardest hit in the first quarter, with relatively limited global impact," the commission said.
Ο Covid-19, which has affected more than 60.000 people and caused more than 1.300 deaths in China, has affected about 30 people in seven The European Union.